Did you Missed Nginx Secure Configuration
by Anish
Posted on Monday July 30, 2018
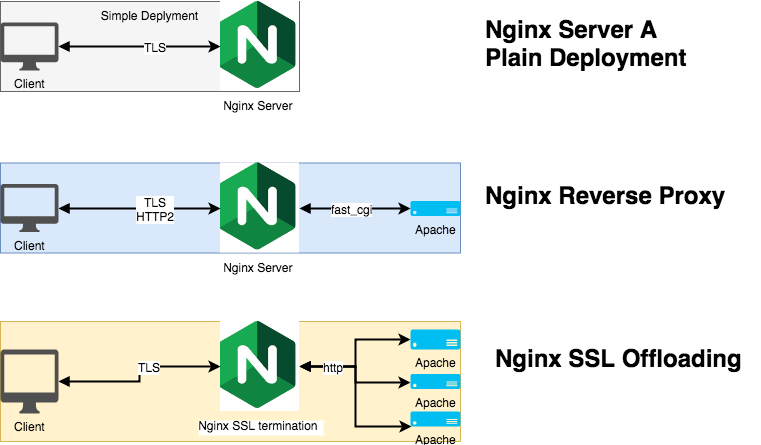
Introduction
This sample chapter extracted from the book, The Modern Cryptograhy CookBook . The Book theme isCryptography is for EveryOne. Learn from Crypto Principle to Applied Cryptography With Practical Example
Get this book on Just $9 by availing coupon discount
In this article we will go through all the nginx Advanced secure configuration, The example shown in this document is for nginx.conf file and can be downloaded from here
What we will cover
| nginx Security | Description |
|---|---|
| Least Privilege | Run nginx as non root |
| Lets encrypt | ACME Directory Creation |
| nginx Header Security | List of HTTP header and Security Configuration |
| nginx TLS Config | Nginx Modern TLS Ciphersuites and Setting |
| HTTP2 Support | Adding HTTP2 Support with TLS |
| OCSP Stapling | OCSP Stapling |
| Handling Buffer Overflow | nginx module client_max_body_size |
| Redirect http to Https | Redirect Configuration from http to Https |
| Subdomain Redirect | Redirect all subdomain to secure location |
| Rate Limiting | Nginx Rate Limit Modules |
| SELinux | selinux changing the folder location |
| Basic Auth | htpasswd and nginx.conf file |
| Syslog Configuration | Redirects logs to syslog |
| Block robots | Block robots/ user-agents |
| Enable Compression | gzip compression for faster HTML response |
| IPv6 Listen | Configure nginx to Listen Over Ipv6 |
| Nginx PHP | Configure nginx for PHP |
| Nginx Wordpress Setting | Configure nginx for wordpress |
| Nginx Drupal Setting | Configure nginx for Drupal |
| Nginx Modularized File Structure | Organize your nginx configuration file in most optimal way |
Nginx Least Priviledge
Always start nginx process with lease privilege principle (non root user) for example user www-data; and define worker_processes to fully use all the available core.
user www-data;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
worker_processes auto;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
OCSP stapling
Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) was created as an alternative to the Certificate Revocation List (CRL) protocol. Both protocols are used to check whether an SSL Certificate has been revoked.
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
Nginx HTTP Header Security Parameter
These security header will be part of every HTTP response
| HTTP Header | Value |
|---|---|
| X-Frame-Options | SAMEORIGIN |
| X-XSS-Protection | “1; mode=block” |
| X-Content-Type-Options | nosniff |
| Referrer-Policy | "no-referrer-when-downgrade |
| Content-Security-Policy | default-src * data: 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline' |
| Strict-Transport-Security | max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload |
| client_max_body_size | 16M |
| servertokens | off |
Sample Configuration in nginx
http{
server_tokens off;
client_max_body_size 16M;
server {
.....
# security headers
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src * data: 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline'" always;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
......
}
}
Nginx Set max POST and GET Size
Sets the maximum allowed size of the client request body, header and buffer size, to prevent any buffer overflow attack
http{
client_max_body_size 16M;
client_header_buffer_size 1k;
client_body_buffer_size 2k;
}
Nginx Rate Limiting
Protect the webserver by rate-limiting in case of DoS or DDoS Attack , Rate limiting is configured with two main directives, limit_req_zone and limit_req, as in this
# limits
limit_req_log_level warn;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=login:10m rate=10r/m;
There could be several limit_req directives. For example, the following configuration will limit the processing rate of requests coming from a single IP address and, at the same time, the request processing rate by the virtual server:
10 MB (10m) will give us enough space to store a history of 160k requests. It will only allow 1 request per second (1r/s).
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m rate=1r/s;
limit_req_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m rate=10r/s;
server {
...
limit_req zone=perip burst=5 nodelay;
limit_req zone=perserver burst=10;
}
Nginx Adding http2 support on SSL
NGINX 1.13.9, released on February 20, 2018, includes support for HTTP/2 server push. change the Listening Port and Enabling HTTP/2
http{
.......
.......
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443
ssl http2;
}
}
Nginx TLS Security Parameter with http2 support
Nginx Modern TLS Security configuration
http{
.......
# SSL
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
# Diffie-Hellman parameter for DHE ciphersuites
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/dhparam.pem;
# Secure Configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
.......
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443
ssl http2;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/example.com/public;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem;
}
}
TLS certificate Provider
In case Certificate Type in your environment is Letsencrypt then create ACME-challenge common directory in nginx
LetsEncrypt configuration
# HTTPS: create Diffie-Hellman keys
openssl dhparam -dsaparam -out /etc/nginx/dhparam.pem 2048
# HTTPS: create ACME-challenge common directory
sudo -u www-data sh -c "mkdir -p /var/www/_letsencrypt"
# HTTPS: certbot (obtain certificates)
# disable before first run: ssl_certificate, ssl_certificate_key, ssl_trusted_certificate
certbot certonly --webroot -d www.example.com --email [email protected] -w /var/www/_letsencrypt -n --agree-tos --force-renewal
Add the ACME-challenge in the nginx.conf
# ACME-challenge
location ^~ /.well-known/acme-challenge/ {
root /var/www/_letsencrypt;
}
For Custom Certificates
In case certificate is Managed by the admin, then using the ssl_certificate and ssl_certificate_key nginx module to pass the certificate and private key information
server {
......
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.key;
......
}
Nginx Redirect http to https
For redirecting HTTP requests to HTTPS, to enforce the use of SSL certificates.
Two Use cases:
All http request and redirect to https
server { listen 80; listen [::]:80; server_name .example.com; # ACME-challenge location ^~ /.well-known/acme-challenge/ { root /var/www/_letsencrypt; } location / { return 301 https://example.com$request_uri; } }
Redirect only specific application for example /admin
server { listen 80; listen [::]:80; server_name .example.com; # ACME-challenge location ^~ /.well-known/acme-challenge/ { root /var/www/_letsencrypt; } location /admin { return 301 https://example.com$request_uri; } location / { try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html; }}
Subdomain Redirect
In case subdomain redirect is required for example *.example.com; to be redirected to secure domain
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name *.example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
Disable Unwanted HTTP Methods
Allow only HTTP Method that are critical to system.
add_header Allow "GET, POST, HEAD" always;
if ( $request_method !~ ^(GET|POST|HEAD)$ ) {
return 405;
}
Basic Auth
The .htpasswd (/etc/nginx/.htpasswd;) file contains username in plain text (unencrypted) and a hashed (encrypted) password. Here’s an example:
$ htpasswd .htpasswd anish
New password:
Re-type new password:
Adding password for user anish
$ cat .htpasswd
anish:$apr1$LYYduqJF$hfJCFCi1YTI0yDKeChe4e0
Always generating crypt hash password considered secure.
htpasswd -nbB anish myPasswod
anish:$2y$05$SlyzABkvPEWrDQYIPX97oer49DXOX5gcD/j2TvfdxhLrw7I.QRV62
For Nginx Basic Auth configure these two AUTH modules
- auth_basic
- authbasicuser_file
Example
location / {
auth_basic "Restricted Content";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
}
Logging to Syslog
nginx configuration for syslog the unix:/dev/log is the UNIX socket
server {
access_log syslog:server=unix:/dev/log;
error_log syslog:server=unix:/dev/log;
}
based on the OS, the logging will be captured on either of these files
/var/log/syslog (Ubuntu)
/var/log/messages (EL-6.x/7.x)
/var/log/secure (EL 5.x)
Enable Compression
Compressing your HTML files is an easy way to reduce the amount of data transferred from NGINX to the browser
gzip gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml application/json application/javascript application/xml+rss application/atom+xml image/svg+xml;
Block unwanted user-agents/robots
Deny Certain User-Agents or Bots. denying user-agents and bots in Nginx it is very easy and can be performed anytime, you can easily block any bots, spammers web-scanners that may attack your server:
if ($http_user_agent ~
(msnbot|Purebot|Baiduspider|Lipperhey|Mail.Ru|scrapbotBaiduspider|Yandex|DirBuster|libwww|"")) {
return 403;
}
Listen to Ipv6
To Listen Secure Server in Ipv6 address
listen 443 ssl;
listen [2001:420:c0e0:1008::33]:443 ssl;
The ipv6 localhost is ::1. The unspecified address is ::
listen [::]:443
Enable SELinux
Ensure that SELinux is running in enforcing mode globally.
setenforce 1
Default SELinux policy labels nginx and its associated files and ports with domain (type) httpd_t. You can use sesearch to investigate the policy and see what port types httpdt can namebind to
sesearch --allow -s httpd_t | grep name_bind
Observed the Output
allow httpd_t http_port_t : tcp_socket name_bind ;
allow httpd_t http_port_t : udp_socket name_bind ;
Check the SELinux Managed ports
semanage port -l | grep http_port_t
http_port_t tcp 80, 443
In case the app directly is moved to new location for example /opt/myapp then user needs to change the semanage fcontext to the new directory followed by restorecon
semanage fcontext -at httpd_sys_rw_content_t "/opt/myapp(/.*)?"
restorecon -R -v '/var/local/myapp'
Full Working Example
Summary of Key Configuration (Least Privilege, server tokens, header security, client limits, server tokesn off , ssl, http2, rate limits )
user www-data;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
worker_processes auto;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events {
multi_accept on;
worker_connections 65535;
}
http {
charset utf-8;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
client_max_body_size 16M;
# MIME
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
# limits
limit_req_log_level warn;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=login:10m rate=10r/m;
# SSL
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
# Diffie-Hellman parameter for DHE ciphersuites
ssl_dhparam /etc/nginx/dhparam.pem;
# Modern TLS configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# OCSP Stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 208.67.222.222 208.67.220.220 valid=60s;
resolver_timeout 2s;
# load configs
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# www.example.com
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name www.example.com;
root /var/www/example.com/public;
# SSL
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem;
# index.html fallback
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
# security headers
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src * data: 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline'" always;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
# . files
location ~ /\. {
deny all;
}
# assets, media
location ~* \.(?:css(\.map)?|js(\.map)?|jpe?g|png|gif|ico|cur|heic|webp|tiff?|mp3|m4a|aac|ogg|midi?|wav|mp4|mov|webm|mpe?g|avi|ogv|flv|wmv)$ {
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# svg, fonts
location ~* \.(?:svgz?|ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff|woff2)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*";
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# gzip
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml application/json application/javascript application/xml+rss application/atom+xml image/svg+xml;
}
# HTTP redirect
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name .example.com;
# ACME-challenge
location ^~ /.well-known/acme-challenge/ {
root /var/www/_letsencrypt;
}
location / {
return 301 https://www.example.com$request_uri;
}
}
}
PHP Nginx Setting
php fastcgi_pass setting for Plain TCP and Various PHP version sockets
| PHP version | fastcgi_pass |
|---|---|
| TCP | 127.0.0.1:9000 |
| PHP 5.x Socket | fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php5-fpm.sock |
| PHP 7.0 Socket | fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.0-fpm.sock |
| PHP 7.1 Socket | fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.1-fpm.sock |
| PHP 7.2 Socket | fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock |
| PHP 7.3 Socket | fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.3-fpm.sock |
Add the location directive for php extensions handlers
server{
........
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
# fastcgi
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PHP_ADMIN_VALUE open_basedir=$base/:/usr/lib/php/:/tmp/;
fastcgi_intercept_errors off;
fastcgi_buffer_size 128k;
fastcgi_buffers 256 16k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
# default fastcgi_params
include fastcgi_params;
}
# . files
location ~ /\. {
deny all;
}
# assets, media
location ~* \.(?:css(\.map)?|js(\.map)?|jpe?g|png|gif|ico|cur|heic|webp|tiff?|mp3|m4a|aac|ogg|midi?|wav|mp4|mov|webm|mpe?g|avi|ogv|flv|wmv)$ {
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# svg, fonts
location ~* \.(?:svgz?|ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff|woff2)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*";
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
......
}
Wordpress Setting
Add additional location directive in addition to the PHP setting , p.s include _php_fastcgi.conf;
# WordPress: allow TinyMCE
location = /wp-includes/js/tinymce/wp-tinymce.php {
include _php_fastcgi.conf;
}
# WordPress: deny wp-content, wp-includes php files
location ~* ^/(?:wp-content|wp-includes)/.*\.php$ {
deny all;
}
# WordPress: deny wp-content/uploads nasty stuff
location ~* ^/wp-content/uploads/.*\.(?:s?html?|php|js|swf)$ {
deny all;
}
# WordPress: deny wp-content/plugins nasty stuff
location ~* ^/wp-content/plugins/.*\.(?!css(\.map)?|js(\.map)?|ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff|woff2|svgz?|jpe?g|png|gif|ico|cur|heic|webp|tiff?|mp3|m4a|aac|ogg|midi?|wav|mp4|mov|webm|mpe?g|avi|ogv|flv|wmv|pdf|docx?|xlsx?|pptx?) {
deny all;
}
# WordPress: deny scripts and styles concat
location ~* \/wp-admin\/load-(?:scripts|styles)\.php {
deny all;
}
# WordPress: deny general stuff
location ~* ^/(?:xmlrpc\.php|wp-links-opml\.php|wp-config\.php|wp-config-sample\.php|wp-comments-post\.php|readme\.html|license\.txt)$ {
deny all;
}
# WordPress: throttle wp-login.php
location = /wp-login.php {
limit_req zone=login burst=2 nodelay;
include _php_fastcgi.conf;
}
The /etc/nginx/phpfastcgi.conf file
try_files $uri =404;
# fastcgi
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php7.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PHP_ADMIN_VALUE open_basedir=$base/:/usr/lib/php/:/tmp/;
fastcgi_intercept_errors off;
fastcgi_buffer_size 128k;
fastcgi_buffers 256 16k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 256k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 256k;
# default fastcgi_params
include fastcgi_params;
Drupal Setting
Add additional location directive in addition to the PHP setting
# Drupal: deny private files
location ~ ^/sites/.*/private/ {
deny all;
}
# Drupal: deny php in files
location ~ ^/sites/[^/]+/files/.*\.php$ {
deny all;
}
# Drupal: deny php in vendor
location ~ /vendor/.*\.php$ {
deny all;
}
# Drupal: throttle user functions
location ~ ^/user/(?:login|register|password) {
limit_req zone=login burst=2 nodelay;
try_files $uri /index.php?$query_string;
}
}
Nginx Modularized File Structure
Maintaining nginx configuration in a single file become cumbersome, if more rules is added , Separate the config file in modularized way
- /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com.conf
- /etc/nginx/_general.conf
The /etc/nginx/nginx.conf file included with sites-enabled directory
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
user www-data;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
worker_processes auto;
worker_rlimit_nofile 65535;
events {
multi_accept on;
worker_connections 65535;
}
http {
charset utf-8;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
server_tokens off;
log_not_found off;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
client_max_body_size 16M;
# MIME
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log warn;
# SSL
ssl_session_timeout 1d;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m;
ssl_session_tickets off;
# modern configuration
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2;
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# OCSP Stapling
ssl_stapling on;
ssl_stapling_verify on;
resolver 8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4 208.67.222.222 208.67.220.220 valid=60s;
resolver_timeout 2s;
# load configs
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
include /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/*;
}
The /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com.conf which include _general.conf;
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name example.com;
root /var/www/example.com;
# SSL
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/example.com.key;
include _general.conf;
}
# HTTP redirect
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name .example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
The /etc/nginx/_general.conf
# security headers
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src * data: 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline'" always;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
# . files
location ~ /\. {
deny all;
}
# assets, media
location ~* \.(?:css(\.map)?|js(\.map)?|jpe?g|png|gif|ico|cur|heic|webp|tiff?|mp3|m4a|aac|ogg|midi?|wav|mp4|mov|webm|mpe?g|avi|ogv|flv|wmv)$ {
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# svg, fonts
location ~* \.(?:svgz?|ttf|ttc|otf|eot|woff|woff2)$ {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin "*";
expires 7d;
access_log off;
}
# gzip
gzip on;
gzip_vary on;
gzip_proxied any;
gzip_comp_level 6;
gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml application/json application/javascript application/xml+rss application/atom+xml image/svg+xml;
Reload /Restart Nginx
After Configuration Verify the Nginx Conf files and then restart it
Check for syntax errors
sudo nginx -t
if no synax error then restart nginx For EL 7.x
sudo systemctl restart nginx
For EL 6.x
sudo service nginx restart
Thanku for reading !!! Give a Share for Support
Your Support Matters!
Instead of directly asking for donations, I'm thrilled to offer you all nine of my books for just $9 on leanpub By grabbing this bundle you not only help cover my coffee, beer, and Amazon bills but also play a crucial role in advancing and refining this project. Your contribution is indispensable, and I'm genuinely grateful for your involvement in this journey!
Any private key value that you enter or we generate is not stored on this site, this tool is provided via an HTTPS URL to ensure that private keys cannot be stolen, for extra security run this software on your network, no cloud dependency
Applied Cryptography Topics
Web Crypto API Topics
Ansible Related Topics
Kubernetes Related Topics
Openstack Articles
Linux Related Topics
python Cryptography Topics
PHP Cryptography Topics
Topics
For Coffee/ Beer/ Amazon Bill and further development of the project Support by Purchasing, The Modern Cryptography CookBook for Just $9 Coupon Price
Kubernetes for DevOps
Hello Dockerfile