Service Mesh With Istio
by Anish
Posted on Tuesday April 9, 2019
Introduction
This sample chapter extracted from the book, Kubernetes for DevOps .
Get this book on Just $9 or Ask Author for Discount
Istio is an open source independent service mesh that provides the fundamentals you need to successfully run a distributed microservice architecture.
A service mesh is a dedicated infrastructure layer for handling service-to-service communication. It's responsible for the reliable delivery of requests through the complex topology of services that comprise a modern, cloud native application.
An Istio service mesh is logically split into a data plane and a control plane.
-
The data plane is composed of a set of intelligent proxies (Envoy) deployed as sidecars. These proxies mediate and control all network communication between microservices along with Mixer, a general-purpose policy and telemetry hub.
-
The control plane manages and configures the proxies to route traffic. Additionally, the control plane configures Mixers to enforce policies and collect telemetry.
Let's review in more detail what each of the components that make up this service mesh are.
-
Envoy
- Processes the inbound/outbound traffic from inter-service and service-to-external-service transparently.
-
Pilot
- Pilot provides service discovery for the Envoy sidecars, traffic management capabilities for intelligent routing (e.g., A/B tests, canary deployments, etc.), and resiliency (timeouts, retries, circuit breakers, etc.)
-
Mixer
- Mixer enforces access control and usage policies across the service mesh, and collects telemetry data from the Envoy proxy and other services.
-
Citadel
- Citadel provides strong service-to-service and end-user authentication with built-in identity and credential management.
Download and Install ISTIO CLI
Before we can get started configuring Istio we'll need to first install the command line tools that you will interact with. To do this run the following
curl -L https://git.io/getLatestIstio | sh -
// version can be different as istio gets upgraded
cd istio-*
sudo mv -v bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/
The output
root@kube-master:~# curl -L https://git.io/getLatestIstio | sh -
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0
100 1631 100 1631 0 0 1849 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1849
Downloading istio-1.1.2 from https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.1.2/istio-1.1.2-linux.tar.gz ...
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
100 614 0 614 0 0 1485 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 1483
100 15.0M 100 15.0M 0 0 8379k 0 0:00:01 0:00:01 --:--:-- 21.5M
Downloaded into istio-1.1.2:
bin install istio-telemetry.yaml istio.VERSION LICENSE README.md samples tools
Add /root/istio-1.1.2/bin to your path; e.g copy paste in your shell and/or ~/.profile:
export PATH="$PATH:/root/istio-1.1.2/bin"
root@kube-master:~# cd istio-*
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# sudo mv -v bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/
'bin/istioctl' -> '/usr/local/bin/istioctl'
INSTALL ISTIO
Define service account for Tiller
- First create a service account for Tiller:
kubectl apply -f install/kubernetes/helm/helm-service-account.yaml
The output
serviceaccount/tiller unchanged
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/tiller unchanged
- Install Istio CRDs
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# helm install install/kubernetes/helm/istio-init --name istio-init --namespace istio-system
- check the Installation
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl get crds | grep 'istio.io'
adapters.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
apikeys.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
attributemanifests.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:01Z
authorizations.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
bypasses.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
checknothings.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
circonuses.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
cloudwatches.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:00Z
clusterrbacconfigs.rbac.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:01Z
deniers.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
destinationrules.networking.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:01Z
dogstatsds.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:00Z
edges.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
envoyfilters.networking.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:01Z
fluentds.config.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:02Z
gateways.networking.istio.io 2019-04-08T12:39:01Z
.....
....
- Finally installs Istio's core components:
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# helm install install/kubernetes/helm/istio --name istio --namespace istio-system --set global.configValidation=false --set sidecarInjectorWebhook.enabled=false --set grafana.enabled=true --set servicegraph.enabled=true
- Verify the services
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl get svc -n istio-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
grafana ClusterIP 10.96.171.173 <none> 3000/TCP 2m40s
istio-citadel ClusterIP 10.96.65.75 <none> 8060/TCP,15014/TCP 2m40s
istio-galley ClusterIP 10.106.97.125 <none> 443/TCP,15014/TCP,9901/TCP 2m40s
istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.102.204.117 172.20.240.112 80:31380/TCP,443:31390/TCP,31400:31400/TCP,15029:30709/TCP,15030:30672/TCP,15031:31789/TCP,15032:32654/TCP,15443:30390/TCP,15020:31778/TCP 2m40s
istio-pilot ClusterIP 10.109.0.98 <none> 15010/TCP,15011/TCP,8080/TCP,15014/TCP 2m40s
istio-policy ClusterIP 10.106.140.39 <none> 9091/TCP,15004/TCP,15014/TCP 2m40s
istio-telemetry ClusterIP 10.98.74.109 <none> 9091/TCP,15004/TCP,15014/TCP,42422/TCP 2m40s
prometheus ClusterIP 10.98.183.129 <none> 9090/TCP 2m40s
servicegraph ClusterIP 10.100.212.98 <none> 8088/TCP
- Verify the pods are in running state.
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-57586c685b-5nsb9 1/1 Running 0 3m25s
istio-citadel-7579f8fbb9-frnqz 1/1 Running 0 3m25s
istio-galley-79d4c5d9f7-llpvk 1/1 Running 0 3m25s
istio-ingressgateway-5fbcf4488f-vzt98 1/1 Running 0 3m25s
istio-init-crd-10-cwn8j 0/1 Completed 0 6m28s
istio-init-crd-11-k4lx4 0/1 Completed 0 6m28s
istio-pilot-df78f86cb-sfzjt 2/2 Running 0 3m25s
istio-policy-5f4747447c-rvt72 2/2 Running 2 3m25s
istio-telemetry-84697c64d7-btbbm 2/2 Running 2 3m25s
prometheus-66c9f5694-lp2wq 1/1 Running 0 3m25s
servicegraph-57d6f5b58c-4m92m 1/1 Running 1 3m24s
DEPLOY SAMPLE APPS
Now that we have all the resources installed for Istio, we will use sample application called BookInfo to review key capabilities of the service mesh such as intelligent routing, and review telemetry data using Prometheus & Grafana.
The Bookinfo application is broken into four separate microservices:
productpage. Theproductpagemicroservice calls thedetailsandreviewsmicroservices to populate the page.details. Thedetailsmicroservice contains book information.reviews. Thereviewsmicroservice contains book reviews. It also calls theratingsmicroservice.ratings. Theratingsmicroservice contains book ranking information that accompanies a book review.
There are 3 versions of the reviews microservice:
- Version v1 doesn't call the
ratingsservice. - Version v2 calls the
ratingsservice, and displays each rating as 1 to 5 black stars. - Version v3 calls the
ratingsservice, and displays each rating as 1 to 5 red stars.
Deploy Sample Apps
- Deploy sample apps by manually injecting istio proxy and confirm pods, services are running correctly
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl apply -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml)
The output
service/details created
deployment.extensions/details-v1 created
service/ratings created
deployment.extensions/ratings-v1 created
service/reviews created
deployment.extensions/reviews-v1 created
deployment.extensions/reviews-v2 created
deployment.extensions/reviews-v3 created
service/productpage created
deployment.extensions/productpage-v1 created
- Verify the book info pod and svc are Running.
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl get pod,svc
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/details-v1-54c6f46b4b-q5b45 2/2 Running 0 58s
pod/my-nginx-6cc48cd8db-n6scm 1/1 Running 4 27d
pod/productpage-v1-5c4f6df4dd-7lcws 2/2 Running 0 58s
pod/ratings-v1-6ccbd9c4f4-2cjbd 2/2 Running 0 58s
pod/reviews-v1-bfc99c79-jhqr6 2/2 Running 0 58s
pod/reviews-v2-6ffb5f6b44-zf9tt 2/2 Running 0 58s
pod/reviews-v3-7c67bd445-bc5ms 2/2 Running 0 58s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/details ClusterIP 10.99.96.161 <none> 9080/TCP 58s
service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 27d
service/productpage ClusterIP 10.106.134.93 <none> 9080/TCP 58s
service/ratings ClusterIP 10.106.213.22 <none> 9080/TCP 58s
service/reviews ClusterIP 10.100.60.83 <none> 9080/TCP 58s
- Define the virtual service and ingress gateway
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
The output
gateway.networking.istio.io/bookinfo-gateway created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/bookinfo created
Testing
To test, do the following:
- Open a new browser tab
- Paste the DNS endpoint returned from the previous
get service istiogatewaycommand - Add /productpage to the end of that DNS endpoint
- Hit enter to retrieve the page.
- Click reload multiple times to see how the layout and content of the reviews changes as differnt versions (v1, v2, v3) of the app are called.
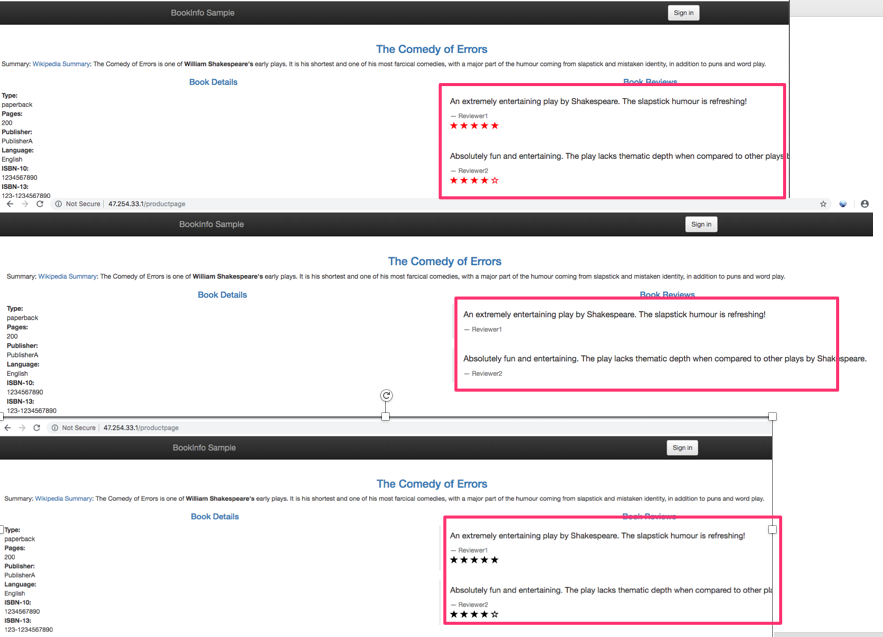
Configuring Request Routing
Service versions (a.k.a. subsets) - In a continuous deployment scenario, a give service can have different subsets and can run different versions of the same application. Common scenarios where this occurs include A/B testing, canary rollouts, etc. The choice of a particular version can be decided based on various criterion (headers, url, etc.) and/or by weights assigned to each version. Each service has a default version consisting of all its instance.
To Demonstrate this behavior
Apply Destination rule
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
The output
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/productpage created
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/reviews created
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/ratings created
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/details created
View Destination rule for bookinfo
kubectl get destinationrules -o yaml
The output
...
...
spec:
host: details
subsets:
- labels:
version: v1
name: v1
- labels:
version: v2
name: v2
spec:
host: productpage
subsets:
- labels:
version: v1
name: v1
spec:
host: ratings
subsets:
- labels:
version: v1
name: v1
- labels:
version: v2
name: v2
- labels:
version: v2-mysql
name: v2-mysql
- labels:
version: v2-mysql-vm
name: v2-mysql-vm
spec:
host: reviews
subsets:
- labels:
version: v1
name: v1
- labels:
version: v2
name: v2
- labels:
version: v3
name: v3
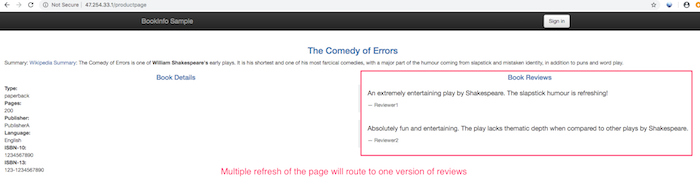
To route to one version only, you apply virtual services that set the default version for the microservices. In this case, the virtual services will route all traffic to reviews:v1 of microservice.
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
The output
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/productpage created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/reviews created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/ratings created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/details created
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl get virtualservices reviews -o yaml
The output
.......
.......
spec:
hosts:
- reviews
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v1
Try now to reload the page multiple times, and note how only version 1 of reviews is displayed each time.
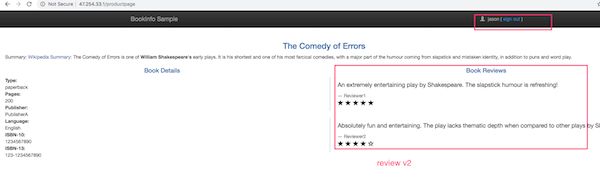
Route based on user identity
User specific routing. In this case, all traffic from a user named Jason will be routed to the service reviews:v2.
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-test-v2.yaml
The output
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/reviews configured
If the user header matches to jason will be routed to the service reviews:v2.
kubectl get virtualservices reviews -o yaml
...........
...........
spec:
hosts:
- reviews
http:
- match:
- headers:
end-user:
exact: jason
route:
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v2
- route:
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v1
Try now by logging with user jason password blank
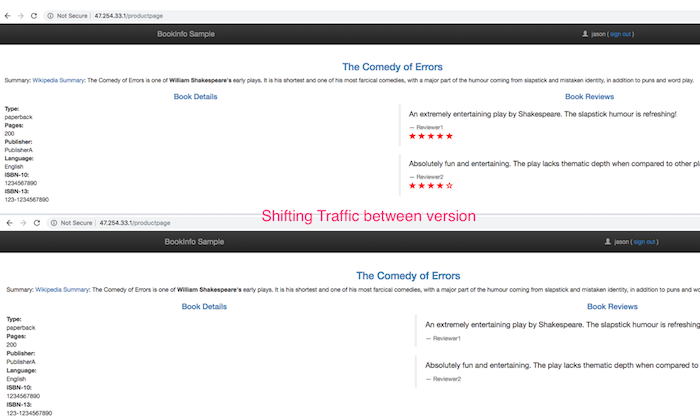
Route based on Traffic
Next, we'll demonstrate how to gradually migrate traffic from one version of a microservice to another. In our example, we'll send 50% of traffic to reviews:v1 and 50% to reviews:v3.
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-reviews-50-v3.yaml
kubectl get virtualservice reviews -o yaml
The subset is set to 50% of traffic to v1 and 50% of traffic to v3 for all reviews request.
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl get virtualservice reviews -o yaml
.............
.............
spec:
hosts:
- reviews
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v1
weight: 50
- destination:
host: reviews
subset: v3
weight: 50
To test it, refresh your browser over and over, and you'll see only reviews:v1 and reviews:v3.
IIstio Monitor And Visualize
First collect new telemetry data and download a YAML file to hold configuration for the new metric and log stream that Istio will generate and collect automatically.
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# curl -LO https://eksworkshop.com/servicemesh/deploy.files/istio-telemetry.yaml
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl apply -f istio-telemetry.yaml
The output
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0
100 2254 100 2254 0 0 3994 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 3996
metric.config.istio.io/doublerequestcount created
prometheus.config.istio.io/doublehandler created
rule.config.istio.io/doubleprom created
logentry.config.istio.io/newlog created
stdio.config.istio.io/newhandler created
rule.config.istio.io/newlogstdio created
Ensure prometheus and grafana services are present
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl -n istio-system get svc prometheus
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
prometheus ClusterIP 10.98.183.129 <none> 9090/TCP 75m
root@kube-master:~/istio-1.1.2# kubectl -n istio-system get svc grafana
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
grafana ClusterIP 10.96.171.173 <none> 3000/TCP 75m
Setup the port forwading for grafana
kubectl -n istio-system port-forward $(kubectl -n istio-system get pod -l app=grafana -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') 8080:3000
The Output
items[0].metadata.name}') 8080:3000
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8080 -> 3000
Open the Grafana UI
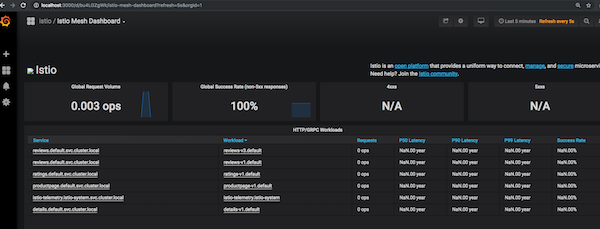
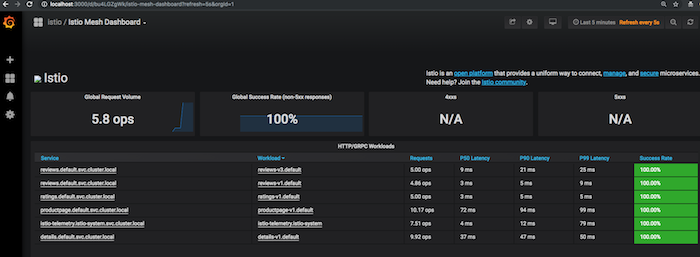
Open a new terminal and send a traffic to the mesh
root@kube-master:~# while true; do curl -o /dev/null -s "172.20.240.112/productpage"; done
Cleanup
To cleanup
- Remove telemetry configuration
- Remove the application virtual services / destination rules
- Remove the gateway
- Remove Istio
kubectl delete -f istio-telemetry.yaml
kubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/networking/virtual-service-all-v1.yaml
kubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
kubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
kubectl delete -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
helm delete --purge istio
helm delete --purge istio-init
Further References
Video Demo
Thanku for reading !!! Give a Share for Support
Your Support Matters!
Instead of directly asking for donations, I'm thrilled to offer you all nine of my books for just $9 on leanpub By grabbing this bundle you not only help cover my coffee, beer, and Amazon bills but also play a crucial role in advancing and refining this project. Your contribution is indispensable, and I'm genuinely grateful for your involvement in this journey!
Any private key value that you enter or we generate is not stored on this site, this tool is provided via an HTTPS URL to ensure that private keys cannot be stolen, for extra security run this software on your network, no cloud dependency
Kubernetes Related Topics
Linux Related Topics
Ansible Related Topics
Openstack Articles
Applied Cryptography Topics
Web Crypto API Topics
python Cryptography Topics
PHP Cryptography Topics
Topics
For Coffee/ Beer/ Amazon Bill and further development of the project Support by Purchasing, The Modern Cryptography CookBook for Just $9 Coupon Price
Kubernetes for DevOps
Hello Dockerfile